Formula 1, il botta e risposta fra Red Bull e McLaren sul T-Tray
Полный Перечень Спорт Ставок Онлайн В Казахстан
December 13, 2022Azərbaycanda Onlayn Kazino Pin Upward Pin Up Slot Maşınlar The Links, IncorporatedDecember 17, 2022
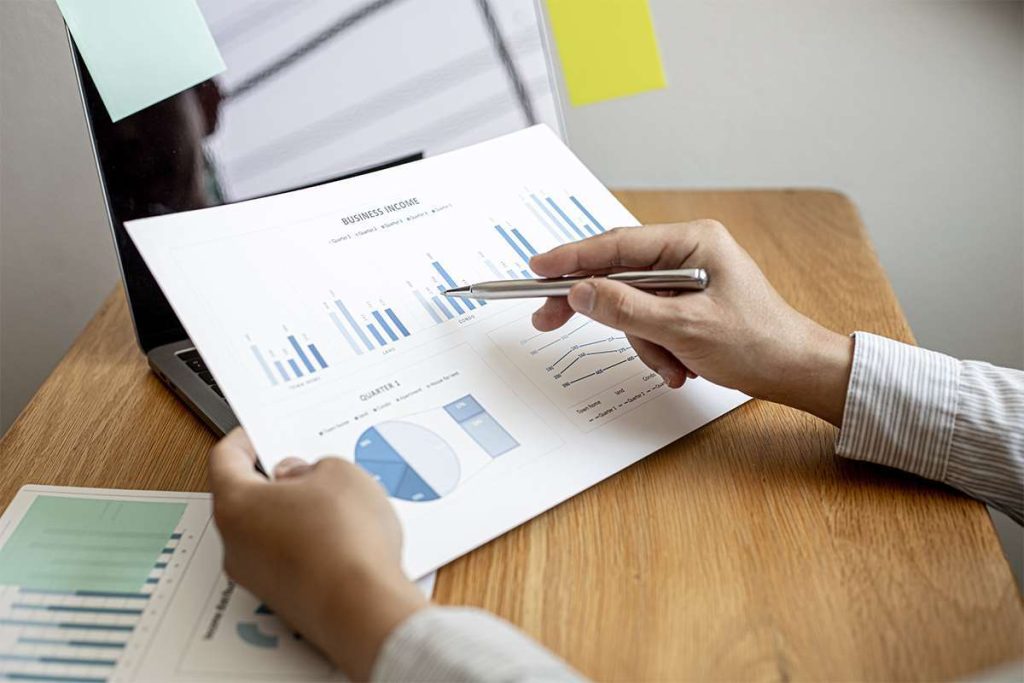

The change in the quantity of units is the difference between the number of units produced at two varying levels of production. Marginal cost strives to be based on a per-unit assumption, so the formula should be used when it is possible for a single additional unit to be produced. The purpose of analyzing marginal cost is to determine at what point an organization can achieve economies of scale to optimize production and overall operations. If the marginal cost of producing one additional unit is lower than the per-unit price, the producer has the potential to gain a profit.

Marginal Cost Example
- When the producer reaches that level at which the cost of producing one extra unit is less than the price of selling one extra unit, they start earning profit.
- Take the Relationship between marginal cost and average total cost graph as a representation.
- Fixed costs are the relatively stable, ongoing costs of operating a business that are not dependent on production levels.
- Marginal cost is strictly an internal reporting calculation that is not required for external financial reporting.
- That is, subtract the quantity from before the increase in production from the quantity from after the increase in production—that will give you the change in quantity.
- The value worked out using calculus differs from the value calculated conventionally because the first derivative provides the instantaneous rate of change of the cost function instead of average change in cost from 14th to 15th unit.
Marginal cost is also beneficial in helping a company take on additional or custom orders. It has additional capacity to manufacture more goods and is approached with an offer to buy 1,000 units for $40 each. Marginal cost is one component needed in analyzing whether it makes sense for the company to accept this order at a special price. McLaren CEO Zak Brown has been vociferously critical of Red Bull’s dual ownership in Formula 1 this season and has called on the FIA to change the rules to ensure all 10 teams are independent. Verstappen, who leads Lando Norris in the drivers championship by 52 points, was surprised to hear his team had been caught up in the clampdown and denied he had derived any performance benefit from the trick part. Several teams had reportedly raised suspicions with the governing body that Red Bull Racing had found a trick way to change its car’s ride height after qualifying.
How to Calculate Marginal Cost?

Fixed costs are the relatively stable, ongoing costs of operating a business that are not dependent on production levels. They include general overhead expenses such as salaries and wages, building rental payments, or utility costs. Variable costs, meanwhile, are those directly related to and those that vary with production levels, such as the cost of materials used in production or the cost of operating machinery in the process of production. Marginal cost is the change of the total cost from an additional output (n+1)th unit. Therefore, (refer to “Average cost” mc formula labelled picture on the right side of the screen. This means that the marginal cost of each additional unit produced is $25.
How to Find Total Cost from Marginal Cost?
Short run marginal cost is the change in total cost when an additional output is produced in the short run and some costs are fixed. On the right side of the page, the short-run marginal cost forms a U-shape, with quantity on the x-axis and cost per unit on the y-axis. In economics, marginal cost is the incremental cost of additional unit of a good.

Sargeant crashed the car in free practice having put a wheel on wet grass on the straight, writing off all its upgrades, and then was uncompetitive in a rebuilt car in the race. Their problems were a consequence of Vowles’ decision to “break so many systems” that had been in place at the team, to try to improve their performance after years of underachievement. Williams, who finished seventh in the constructors’ championship in 2023, had a difficult start to the season, scoring points only twice in the first 15 grands prix. He also reflects on working with the likes of Jenson Button, Daniel Ricciardo and Carlos Sainz, as well as giving an insight into how Oscar Piastri is galvanising the team now.
Relationship between marginal cost and average total cost
The marginal cost of production is calculated whenever productivity levels change. This allows businesses to determine a profit margin and make plans for becoming more competitive to improve profitability. Of all the different categories of costs discussed by economists, including total cost, total variable cost, total fixed cost, etc., marginal cost https://www.bookstime.com/articles/variable-cost is arguably the most important.
- For example, while a monopoly has an MC curve, it does not have a supply curve.
- The marginal cost of production is affected by many factors labor and raw material cost, or cost of energy consumption.
- Red Bull Racing has admitted a recent rules crackdown by the FIA has forced it to make changes to its car ahead of the final six races of the season.
- The Australian suggested after the race that the late call had been at least in part motivated to help the Dutchman, whose Red Bull Racing team is owned by the same Austrian energy drinks company as Ricciardo’s former RB squad.
- But to have four teams that can win any weekend eight drivers, I don’t know which of these four teams might win.
How to Find Variable Cost from Marginal Cost?
Marginal cost is the cost to produce one additional unit of production. It is an important concept in cost accounting, as marginal cost helps determine the most efficient level of production for a manufacturing process. It is calculated by determining what expenses are https://x.com/BooksTimeInc incurred if only one additional unit is manufactured.

Stallard talks about his gruelling fitness regime as an Olympic rower and what a race engineer’s relationship with their driver is all about. So why did Stallard make such a big career change, and how does working in F1 compare to rowing? On the latest episode of Beyond The Grid, he joins host Tom Clarkson at McLaren’s headquarters to discuss this and much more. Tom Stallard, Oscar Piastri’s race engineer and McLaren’s Director of Human Performance, is a man of many talents. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site’s Terms of Service.
